Android Malware Konfety: Evading Detection with Decoy Apps
Android Malware: Konfety's Evasion Techniques

A new variant of the Konfety Android malware has been identified using a malformed ZIP structure and other obfuscation methods that allow it to evade detection. This malware poses as legitimate apps, mimicking products available on Google Play, while lacking the promised functionality. It can redirect users to malicious sites, push unwanted app installs, and deliver fake browser notifications. Moreover, it utilizes the CaramelAds SDK to fetch hidden ads and exfiltrate sensitive information, including installed apps and system details.
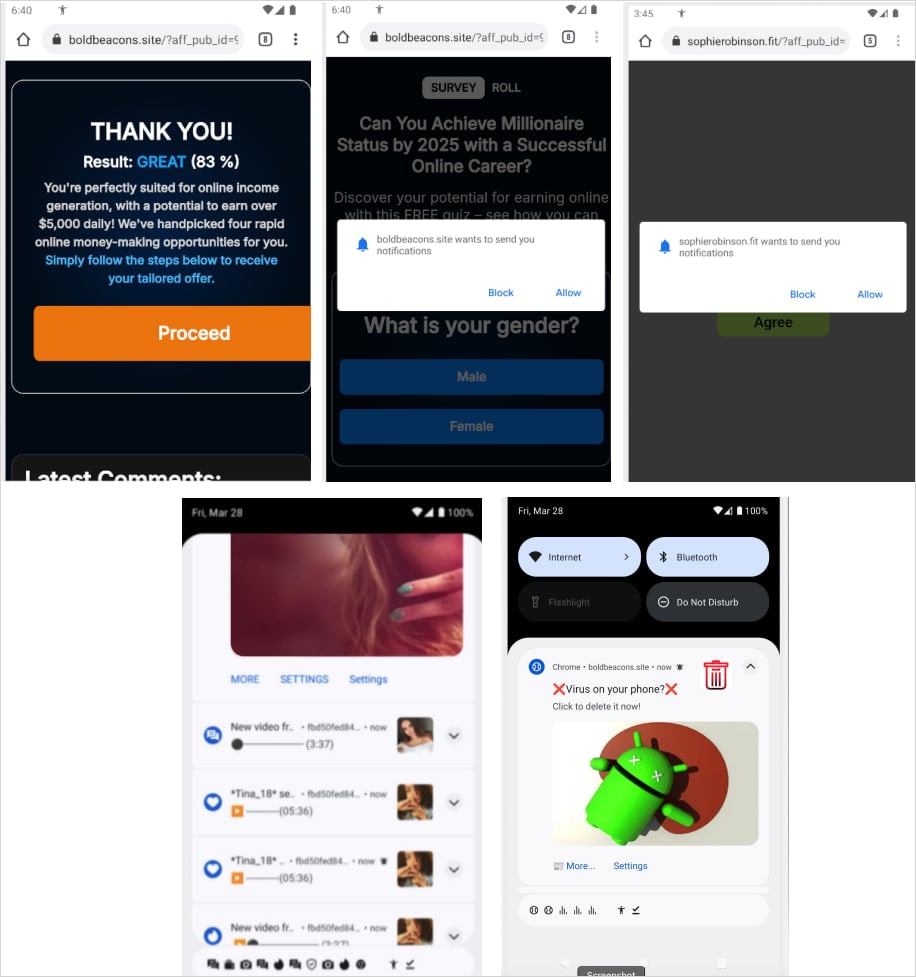
Konfety includes an encrypted secondary DEX file within its APK, which is decrypted at runtime. This allows the installation of additional malicious modules dynamically. Researchers from Zimperium have analyzed Konfety’s techniques, which include copying names and branding of real apps and distributing via third-party stores, known as the "evil twin" tactic.
Evasion Tactics
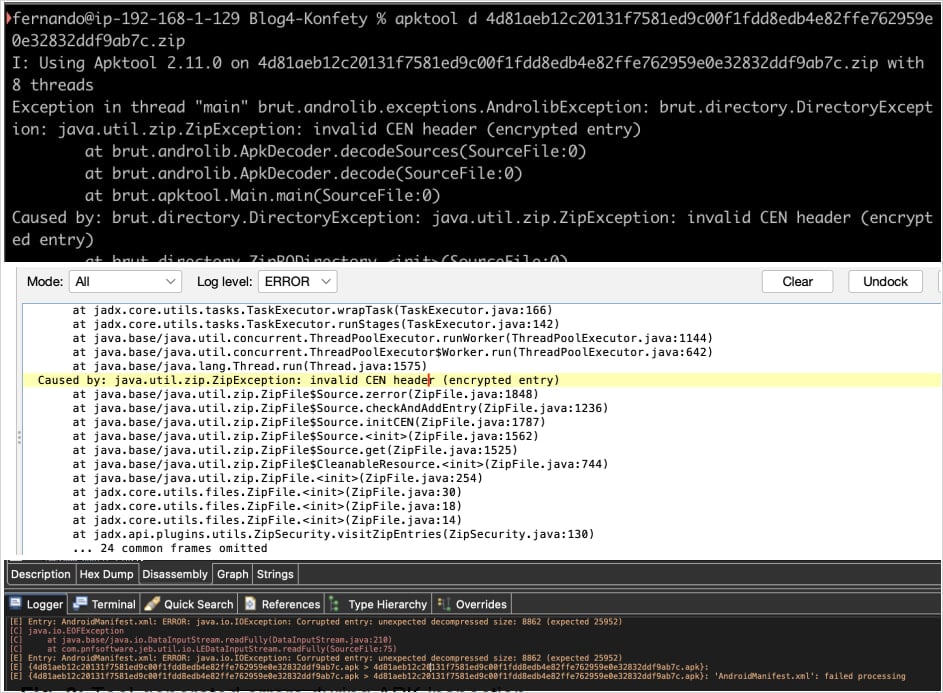
The malware employs several advanced techniques to prevent detection and analysis. It uses dynamic code loading to hide malicious logic in an encrypted DEX file and obfuscates its APK by signaling that the file is encrypted when it is not. This confuses static analysis tools, which trigger false password prompts, blocking access to the APK's contents.
Additionally, critical files within the APK are declared using BZIP compression, which is unsupported by analysis tools like APKTool and JADX, leading to parsing failures. As a result, Android defaults to its processing methods, allowing the malware to install and run without issues.
After installation, Konfety hides its app icon and name, implementing geofencing to change behavior based on the victim's location. Previous reports, such as the one on SoumniBot malware, have noted similar compression-based obfuscation techniques.
Mitigation Strategies
To protect against the Konfety malware and similar strains, it is crucial to avoid sideloading apps. Applications downloaded from third-party stores lack the security checks present in official marketplaces like Google Play Store. Always ensure that Google Play Protect is activated on your device, as it scans apps for malware.
For additional protection, consider installing one of the best Android antivirus apps. Regularly vet each app before installation, as malicious apps often disguise themselves as legitimate software.
GodFather Banking Malware: A New Threat

Zimperium zLabs has uncovered an evolution of the GodFather banking malware, utilizing an advanced on-device virtualization technique to target banking and cryptocurrency applications. This technique allows the malware to create a complete isolated virtual environment on the victim's device, where it can hijack legitimate applications.
The GodFather malware installs a malicious host application that downloads and runs a copy of the targeted app within a controlled sandbox. This method enables attackers to intercept credentials and sensitive data in real-time, rendering traditional security measures ineffective. The malware's ability to manipulate the user experience and bypass security checks marks a significant advance in mobile threats.
Technical Analysis
GodFather employs ZIP manipulation techniques to bypass static analysis tools. Key characteristics include enabling the General Purpose flag in APKs, tricking analysis tools into believing the files are encrypted, and adding misleading field names to obstruct analysis.
The malware utilizes accessibility services to commit fraud, obfuscating its manifest with irrelevant permissions to hinder static analysis. Furthermore, much of the malicious code has been shifted from the native layer to the Java layer, increasing its evasion capabilities.
Command and Control Communication
Critical information, including command and control (C&C) communication details, is stored in shared preferences. The malware uses a Base64-encoded C2 URL embedded in these preferences to connect to its command server. Upon obtaining accessibility permissions, the malware captures screen data, including tap events, allowing it to monitor user interactions continuously.
Overlay Attacks
GodFather utilizes various legitimate open-source tools for its overlay attacks, exploiting their capabilities to virtualize apps and hook into application programming interfaces (APIs). This sophisticated method enables the malware to seamlessly integrate and run deceptive banking apps, posing a significant threat to users.
Konfety Ad Fraud Operation
The Konfety malware has been revealed as part of a large ad fraud operation, leveraging over 250 apps on the Google Play Store to manipulate ad traffic. This campaign utilizes "evil twin" versions of legitimate apps to facilitate ad fraud, where the malicious apps resemble their decoy counterparts by copying their app IDs and publisher IDs.
Researchers from HUMAN reported that these evil twin apps are distributed through malvertising campaigns, tricking users into downloading software that subsequently performs nefarious activities, including ad fraud and data exfiltration.
Users are advised to be cautious and only download apps from legitimate app stores, ensuring that security measures like Google Play Protect are activated. With the continuous evolution of malware tactics, remaining vigilant is essential for safeguarding personal data and device security.
Explore our services at Gopher Security , or contact us for more information on how we can help you enhance your mobile security.





