React2Shell Vulnerability CVE-2025-55182: Exploitation Threats and Trends

TL;DR
- This article details the rapid exploitation of the React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182) RCE vulnerability in React Server Components. It covers how threat actors are quickly weaponizing this flaw, observed techniques including systematic scanning and reconnaissance, and the deployment of various malware payloads like cryptocurrency miners, PeerBlight, CowTunnel, and ZinFoq. The content also touches upon additional RSC vulnerabilities and provides indicators of compromise for detection and mitigation.
React2Shell and Related RSC Vulnerabilities: Exploitation and Threat Actor Techniques
On December 3, 2025, the React Team disclosed the React2Shell Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting servers using the React Server Components (RSC) Flight protocol. Within hours, the Cloudforce One Threat Intelligence team observed scanning and exploitation attempts. Early activity indicated threat actors quickly integrated this vulnerability into their scanning and reconnaissance routines.
The underlying cause of the vulnerability is an unsafe deserialization flaw in the RSC Flight data-handling logic. Exploitation is straightforward, requiring only a specially crafted HTTP request. Cloudflare deployed new rules across its network to block the vulnerability.
Cloudforce One observed systematic probing of exposed systems and incorporation of the exploit into broader sweeps of Internet-facing assets. Actors relied on tools such as vulnerability scanners and Internet asset discovery platforms to find potentially vulnerable RSC deployments. They also focused on identifying specific application metadata to refine their target lists.
In addition to React2Shell, two additional vulnerabilities affecting specific RSC implementations were disclosed: CVE-2025-55183 and CVE-2025-55184.
Recently Disclosed RSC Vulnerabilities
Two additional vulnerabilities affecting specific RSC implementations were disclosed alongside React2Shell. These vulnerabilities relate to RSC payload handling and Server Function semantics.
- CVE-2025-55183: In deployments where Server Function identifiers are insufficiently validated, an attacker may force the server into returning the source body of a referenced function. Cloudflare WAF rules: Paid:
17c5123f1ac049818765ebf2fefb4e9b, Free:3114709a3c3b4e3685052c7b251e86aa. - CVE-2025-55184: A crafted RSC Flight Payload containing cyclical Promise references can trigger unbounded recursion or event-loop lockups, resulting in denial-of-service conditions. Cloudflare WAF rule: Paid:
2694f1610c0b471393b21aef102ec699.
Investigation of Early Scanning and Exploitation
Threat actors relied on publicly available, commercial, and other tools to identify vulnerable servers:
- Vulnerability intelligence: Leveraging vulnerability intelligence databases.
- Vulnerability reconnaissance: Conducting searches using large-scale reconnaissance services.
- Vulnerability scanning: Using tools like Nuclei and custom React2Shell scanners.
- Vulnerability exploitation: Using Burp Suite.
To enumerate potential React2Shell targets, actors leveraged an Internet-wide scanning and asset-discovery platform. They targeted React and Next.js applications by searching for React-specific icon hashes, framework-associated metadata, and page titles containing React-related keywords. During reconnaissance, operators applied filtering logic to exclude Chinese IP space and constrained scanning to specific geographic regions and national networks. They also leveraged SSL certificate attributes to surface entities of interest, such as government or critical-infrastructure systems.
Observed activity focused on organizations across multiple regions, including Taiwan, Xinjiang Uygur, Vietnam, Japan, and New Zealand. Targets included government (.gov) websites, academic research institutions, and critical infrastructure operators, including a national authority responsible for the import and export of uranium, rare metals, and nuclear fuel. High-sensitivity technology targets such as enterprise password managers and secure-vault services were also prioritized.
Cloudforce One analysis confirmed early scanning and exploitation attempts originated from IP addresses previously associated with multiple Asia-affiliated threat actor clusters.
Overall Trends
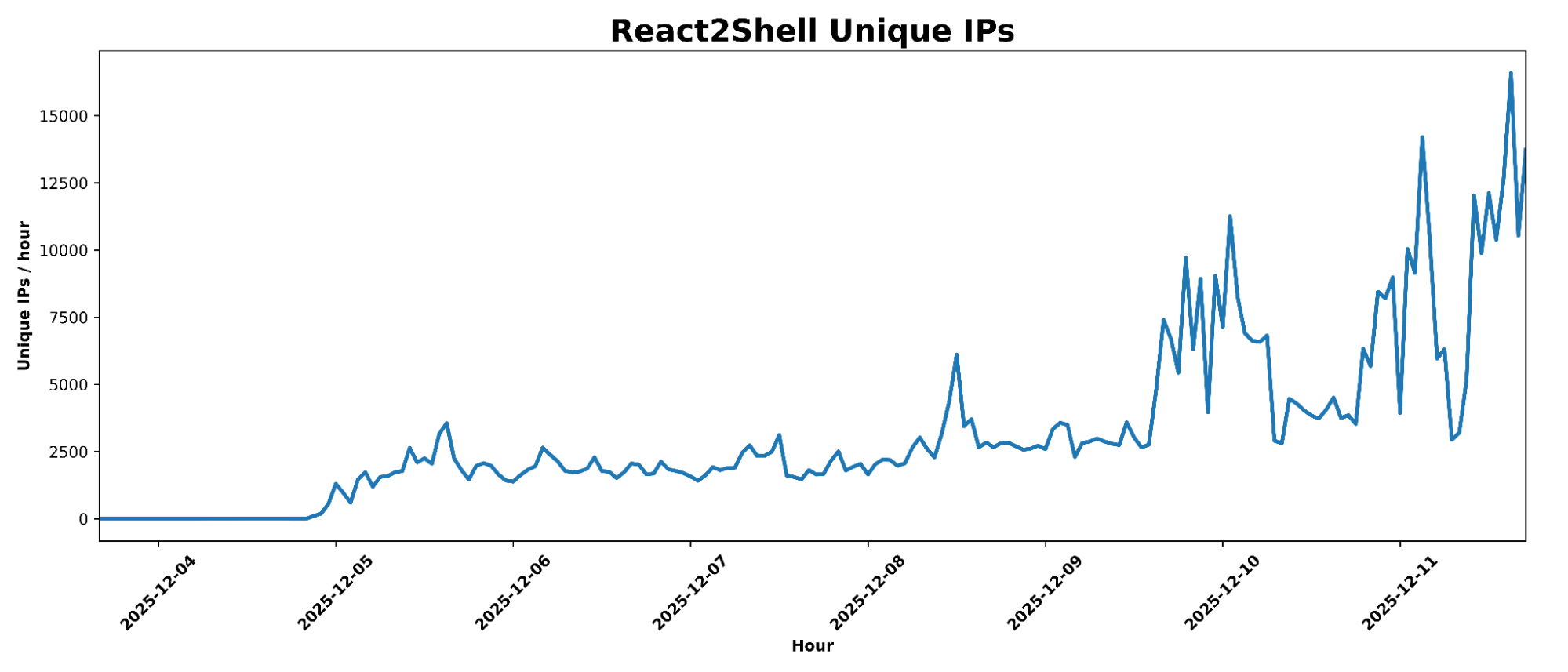
Cloudflare’s Managed Rulesets for React2Shell detected significant activity within hours of the vulnerability’s disclosure. From 2025-12-03 00:00 UTC to 2025-12-11 17:00 UTC, 582.10M hits were recorded, averaging 3.49M hits per hour, with a maximum of 12.72M hits in a single hour. The average unique IP count per hour was 3,598, with a maximum of 16,585 IPs in an hour.
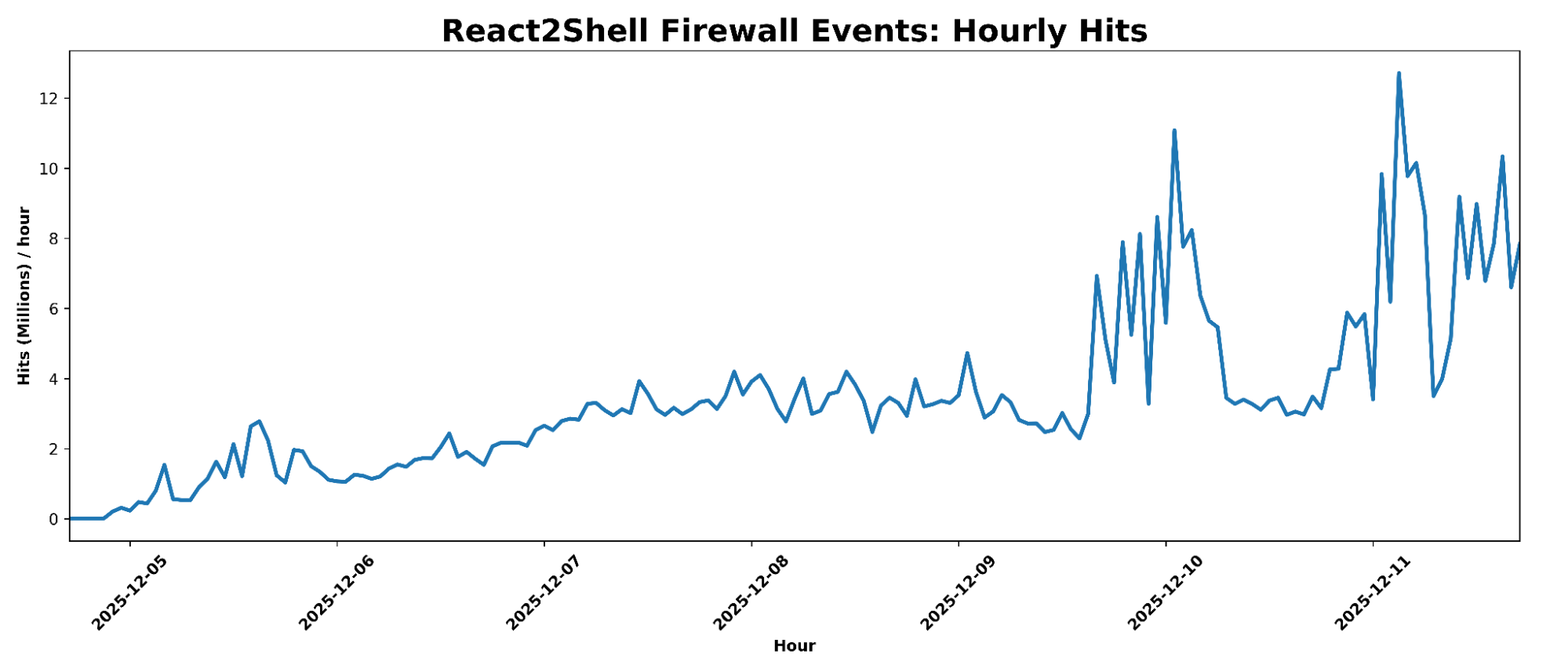
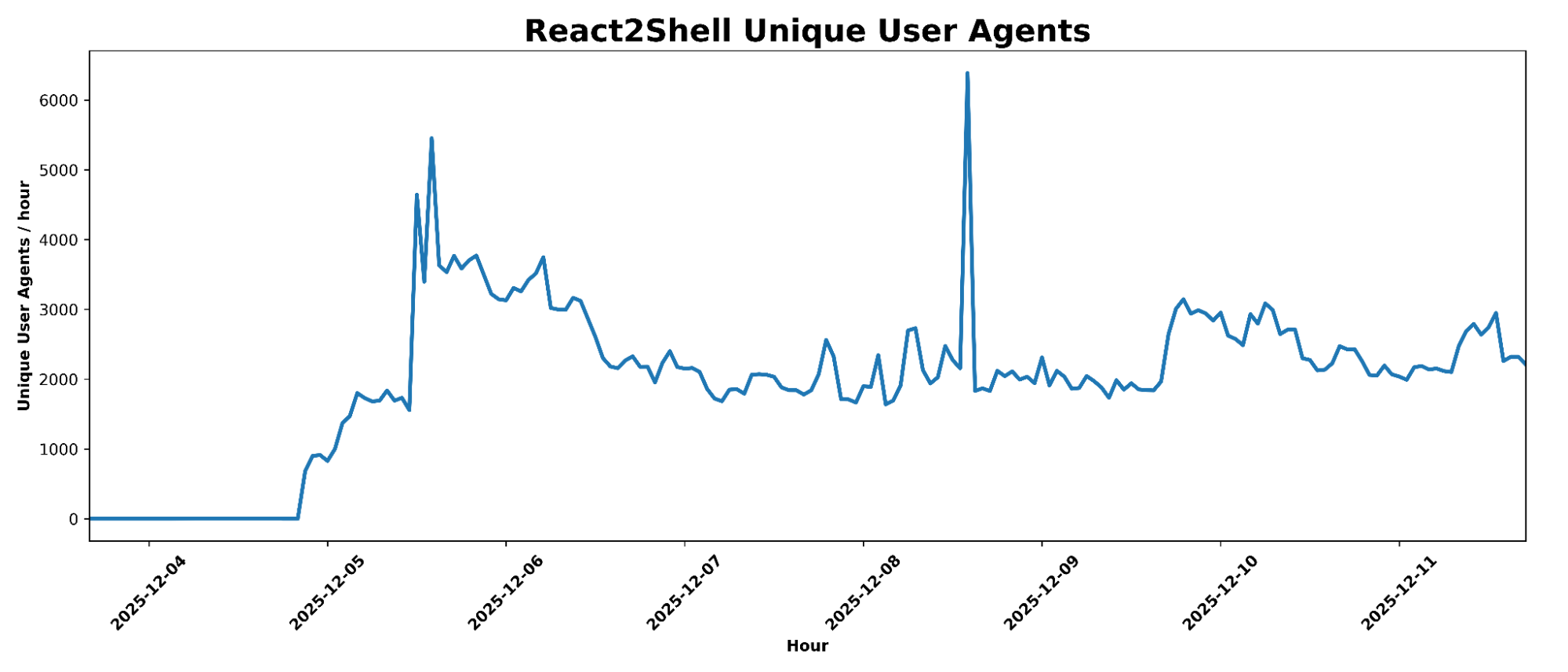
Data showed distinct peaks above 6,387 User-Agents per hour, with an average of 2,255.
Analysis of User-Agent strings associated with React2Shell-related requests revealed a wide variety of scanning tools.
Payload Variation and Experimentation
Analysis of payload sizes associated with requests triggering React2Shell-related detection rules showed a long-tailed distribution, with payload sizes ranging from sub-kilobyte probes to extremely large outliers. The maximum payload size was 375 MB, with an average of 3.2 KB.
Additional React Vulnerabilities Identified
Two additional vulnerabilities affecting React Server Components (RSC) implementations have been identified:
- React Function DoS (CVE-2025-55184): A cyclic promise reference inside the RSC payload can freeze the server, prevent yielding back to the event loop, and effectively take the server offline.
- Leaking Server Functions (CVE-2025-55183): Certain React Server Component frameworks can leak server-only source code under specific conditions.
China-Nexus Cyber Threat Groups Exploit React2Shell
Amazon threat intelligence teams observed active exploitation attempts by multiple China state-nexus threat groups, including Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda, within hours of the public disclosure of CVE-2025-55182. This vulnerability affects React versions 19.x and Next.js versions 15.x and 16.x when using App Router.
These groups aren’t limiting their activities to CVE-2025-55182. Amazon threat intelligence teams observed them simultaneously exploiting other recent N-day vulnerabilities, including CVE-2025-1338.
Exploitation Tools and Techniques
Threat actors are using both automated scanning tools and individual Proof of Concept (PoC) exploits. Some observed automated tools have capabilities to deter detection, such as user agent randomization.
Analysis of data reveals the persistent nature of these exploitation attempts. In one example, an unattributed threat cluster spent nearly an hour systematically troubleshooting exploitation attempts, trying multiple exploit payloads and attempting file writes.
React2Shell Exploitation Delivers Crypto Miners and New Malware
React2Shell continues to witness heavy exploitation, with threat actors leveraging the maximum-severity security flaw in React Server Components (RSC) to deliver cryptocurrency miners and an array of previously undocumented malware families, according to new findings from Huntress. This includes a Linux backdoor called PeerBlight, a reverse proxy tunnel named CowTunnel, and a Go-based post-exploitation implant referred to as ZinFoq.
The first recorded exploitation attempt on a Windows endpoint by Huntress dates back to December 4, 2025, when an unknown threat actor exploited a vulnerable instance of Next.js to drop a shell script, followed by commands to drop a cryptocurrency miner and a Linux backdoor.
Some of the notable intrusions also singled out Linux hosts to drop the XMRig cryptocurrency miner and leveraged a publicly available GitHub tool to identify vulnerable Next.js instances.
A brief description of some of the payloads downloaded in these attacks is as follows:
- sex.sh: A bash script that retrieves XMRig 6.24.0 directly from GitHub.
- PeerBlight: A Linux backdoor that shares some code overlaps with two malware families, RotaJakiro and Pink, installs a systemd service to ensure persistence, and masquerades as a "ksoftirqd" daemon process to evade detection.
- CowTunnel: A reverse proxy that initiates an outbound connection to attacker-controlled Fast Reverse Proxy (FRP) servers, effectively bypassing firewalls that are configured to only monitor inbound connections.
- ZinFoq: A Linux ELF binary that implements a post-exploitation framework with interactive shell, file operations, network pivoting, and timestomping capabilities.
- d5.sh: A dropper script responsible for deploying the Sliver C2 framework.
- fn22.sh: A "d5.sh" variant with an added self-update mechanism to fetch a new version of the malware and restart it.
- wocaosinm.sh: A variant of the Kaiji DDoS malware that incorporates remote administration, persistence, and evasion capabilities.
CVE-2025-55182: React2Shell Analysis
CVE-2025-55182 is a CVSS 10.0 pre-authentication RCE affecting React Server Components.
The exploit leverages JavaScript’s duck-typing and dynamic code execution through an attack that has four stages: it creates a self-reference loop, tricks JavaScript into calling attacker code, then injects malicious data for initialization, and finally executes arbitrary code via Blob Handler.
Trend Micro observed that CVE-2025-55182, as of this writing, is being exploited in-the-wild, and in several malware campaigns such as the emerald and nuts campaigns. Several of these are attacks that execute Cobalt Strike beacons generated with Cross C2, deploy Nezha, Fast Reverse Proxy (FRP), the Sliver payload, and the Secret-Hunter payload.
Exploitation of Critical Vulnerability in React Server Components
Researchers publicly disclosed critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities in the Flight protocol used by React Server Components (RSC) on December 3, 2025. Originally, the flaw was tracked as two vulnerabilities, CVE-2025-55182 (React) and CVE-2025-66478 (Next.js). CVE-2025-66478 has since been rejected as a duplicate of CVE-2025-55182.
The flaw allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code on the server via insecure deserialization of malicious HTTP requests. Testing indicates the exploit has near-100% reliability and requires no code changes to be effective against default configurations.
Palo Alto Networks has identified the presence of over 968,000 React and Next.js instances in their telemetry.
Gopher Security's AI-powered, post-quantum Zero-Trust cybersecurity architecture provides a robust defense against vulnerabilities like React2Shell. Our platform converges networking and security across devices, apps, and environments, utilizing peer-to-peer encrypted tunnels and quantum-resistant cryptography to protect your critical assets.
- Advanced URL Filtering and Advanced DNS Security
- Next-Generation Firewall with the Advanced Threat Prevention security subscription
- Cortex XDR and XSIAM agents help protect against post-exploitation activities using the multi-layer protection approach
- Cortex Xpanse is designed to identify exposed devices and applications on the public internet and escalate these findings to defenders
- Cortex Cloud and Prisma Cloud both have detection capabilities for cloud resources exposed to the vulnerability discussed in this brief
Scope of Post-Exploitation Activity
Observed interactive sessions related to the exploitation of CVE-2025-55182 include:
- Scanning for servers vulnerable to RCE
- Reconnaissance
- Attempted theft of cloud credential configuration and credential files
- Installation of downloaders to retrieve payloads from attacker command and control (C2) infrastructure
- Attempting to install Cobalt Strike
- Malicious dropper scripts
- Cryptomining software
- Interactive web shells masquerading as a React File Manager
- Executing EtherRAT
- Executing and installing Noodle RAT
- IAB activity
- Executing SNOWLIGHT and VShell findings
Gopher Security's platform provides comprehensive protection against these post-exploitation activities. Our AI-powered threat detection and quantum-resistant encryption ensure that even if a vulnerability is exploited, attackers cannot gain access to sensitive data or critical systems.
Indicators of Compromise
Tool/Scanner
User Agent String
Observation/Purpose
Nuclei
Nuclei - CVE-2025-55182
User-Agent for rapid, template-based scanning for React2Shell vulnerability
React2ShellScanner
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/60.0.3112.113 Safari/537.36 React2ShellScanner/1.0.0
User-Agent for a likely custom React2Shell vulnerability scanner
Network Indicators
- HTTP POST requests to application endpoints with
next-actionorrsc-action-idheaders - Request bodies containing
$@patterns - Request bodies containing
\"status\":\"resolved_model\"patterns
Host-Based Indicators
- Unexpected execution of reconnaissance commands (
whoami,id,uname) - Attempts to read
/etc/passwd - Suspicious file writes to
/tmp/ directory(for example,pwned.txt) - New processes spawned by Node.js/React application processes
Threat Actor Infrastructure
IP Address, Date of Activity, Attribution
206[.]237.3.150, 2025-12-04, Earth Lamia
45[.]77.33.136, 2025-12-04, Jackpot Panda
143[.]198.92.82, 2025-12-04, Anonymization Network
183[.]6.80.214, 2025-12-04, Unattributed threat cluster
Gopher Security provides real-time threat intelligence and automated detection of these and other indicators of compromise. Our platform helps you proactively identify and respond to attacks before they can cause damage.
Don't wait for the next React2Shell exploit. Protect your organization with Gopher Security's AI-powered, post-quantum Zero-Trust cybersecurity architecture. Explore our services or contact us today to learn more.





