Understanding DNS Tunneling: Risks, Examples, and Protection Tips
Malware Embedded in DNS
DomainTools reported that malware can now be embedded within Domain Name System (DNS) records, raising concerns about its security and potential for abuse. DNS is essential for translating domain names, like "example.com," into IP addresses, enabling users to access websites without needing to remember numerical addresses. However, this system has become a target for malicious actors.

The exploitation of DNS records began when Ben Cartwright-Cox proposed a file system using DNS as a base. This led to reports of hackers hiding images within DNS records, prompting DomainTools to search for executable file types within DNS records. Their findings indicated that a malicious actor was using DNS TXT records to store and potentially deliver joke malware, known for causing system disturbances and displaying fake error messages.
For further details, see the original reports from DomainTools here and Cyber Security News here.
DNS Exploitation Techniques
Hackers are increasingly using DNS records to hide malware, allowing them to bypass traditional defenses. DomainTools noted that this method enables malware to be fetched without raising alarms, as DNS traffic often goes unmonitored compared to web and email traffic. Specifically, researchers identified a malicious binary for Joke Screenmate stashed in various DNS records, demonstrating how hex-encoded malware can be spread via DNS.

The technique involves breaking malware into chunks and embedding them within the DNS records of a domain, such as whitetreecollective.com. Each chunk is stored in a TXT record, which typically holds arbitrary text. Once an attacker gains access to a network, they can reconstruct the malware by querying these chunks through DNS requests. Ian Campbell from DomainTools highlighted the difficulty organizations face in monitoring DNS traffic, especially with the rise of encrypted DNS traffic via DOH (DNS over HTTPS) and DOT (DNS over TLS).
For more comprehensive insights, refer to Ars Technica’s article here and DomainTools' findings here.
DNS Tunneling Attacks
DNS tunneling attacks exploit the DNS protocol to create covert communication channels for malicious activities. This technique allows cybercriminals to bypass security measures, executing commands and extracting data without detection. The inherent trust in DNS makes it a prime target for such attacks.
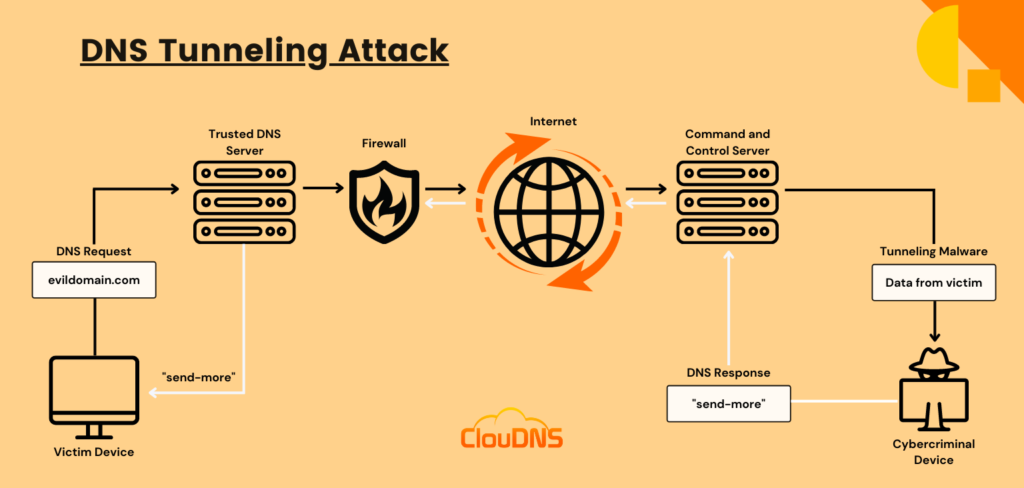
In a typical DNS tunneling scenario, an attacker registers a domain and configures a server to receive DNS queries from compromised devices. These queries carry encoded commands that the attacker can use to control the infected system. Despite the effectiveness of DNS tunneling, many organizations neglect monitoring DNS traffic, focusing instead on web and email security.
To detect DNS tunneling, organizations can analyze DNS payloads for anomalies, monitor traffic volume from specific IP addresses, and check for unusual patterns in DNS queries. For more information on DNS tunneling, refer to the ClouDNS blog here.
Mitigating DNS Tunneling Risks
To combat DNS tunneling, organizations need to enhance their monitoring and detection capabilities. Implementing a DNS firewall can help identify and block malicious domains, while regular vulnerability assessments can uncover weak points in a network's defenses.
Best practices include:
- Directing all internal DNS requests through designated internal servers to filter potential threats.
- Monitoring DNS traffic for unusual patterns or spikes.
- Training staff to recognize and report suspicious activities.
For extensive guidelines on preventing DNS tunneling attacks, refer to Palo Alto Networks here and ClouDNS monitoring services here.
For further information on securing your DNS infrastructure and protecting against various cyber threats, explore our services at undefined or contact us at undefined.





