WhatsApp Security Flaw Exposes 3.5 Billion User Phone Numbers

TL;DR
- Researchers uncovered a critical WhatsApp security flaw, enabling the enumeration of 3.5 billion phone numbers and associated profile data like photos and 'About' text. This vulnerability poses significant privacy risks, including targeted attacks and potential persecution in restricted regions. While Meta is implementing countermeasures, the incident highlights the ongoing need for enhanced security measures.
WhatsApp Security Flaw Exposes Billions of Phone Numbers
Researchers have discovered a significant privacy flaw in WhatsApp's contact discovery mechanism, potentially exposing the phone numbers of over 3.5 billion users. This vulnerability allowed researchers to enumerate active accounts and access associated data, raising concerns about user privacy and security.
Vulnerability Details
A team from the University of Vienna and SBA Research identified a flaw in WhatsApp’s contact discovery mechanism. This mechanism, designed to match mobile numbers in a user’s address book with corresponding numbers in WhatsApp’s database, was abused to confirm the existence of mobile numbers associated with WhatsApp across 245 countries. The researchers were able to confirm 3.5 billion mobile numbers registered to the platform, exceeding previous estimates.
The vulnerability allowed researchers to query over 100 million phone numbers per hour from a single IP address. This was achieved by reverse-engineering WhatsApp’s API and using tools like libphonegen and a modified open-source client named whatsmeow. At its peak, the team was confirming 7,000 numbers per second without being blocked.
Data Exposure
The researchers were able to access not only phone numbers but also other data, including:
- Profile photos (57% of users)
- "About" text (29% of users)
- Encryption keys
This exposed data allowed the researchers to infer metadata such as the user’s device operating system, the age of the account, and the number of linked secondary devices. Knowing whether a specific phone number is linked to a messaging app can be highly sensitive, especially in regions where certain messaging apps are banned.
Meta's Response and Mitigation
Meta, WhatsApp’s parent company, was informed of the vulnerability through their bug bounty program. According to SBA Research, Meta has implemented countermeasures such as rate-limiting and stricter visibility rules for profile information.
However, the researchers noted that Meta's response was slow, with the company barely acknowledging the issue for a year after it was first reported in September 2024. Meta stated that they had already been working on anti-scraping systems and found no evidence of malicious actors abusing this vector.
Broader Implications
The exposure of phone numbers and associated data can have significant implications:
- Targeted Attacks: Confirmed active mobile numbers can become targets for spam, phishing, and robocalling. A previous 2021 Facebook hack revealed that 58% of the leaked phone numbers remain active on WhatsApp.
- Privacy Risks: In countries where WhatsApp is banned, such as China and Myanmar, the ability to identify users can lead to serious consequences, including state surveillance and persecution.
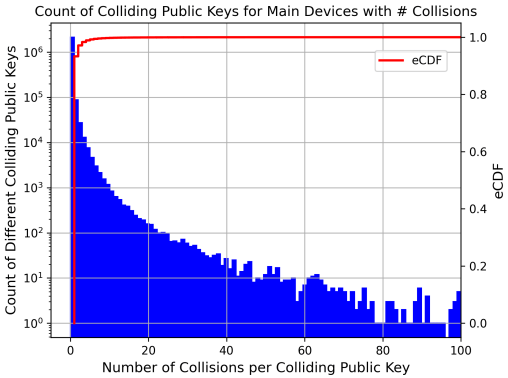
- Compromised Encryption: The discovery of 'public key collisions,' where some users are using weak or non-unique key pairs, raises concerns about the security of end-to-end encryption.
Mitigation with Zero-Trust Architecture
This incident highlights the importance of robust security measures to protect user data. At Gopher Security, we specialize in AI-powered, post-quantum Zero-Trust cybersecurity architecture. Our platform converges networking and security across devices, apps, and environments—from endpoints and private networks to cloud, remote access, and containers—using peer-to-peer encrypted tunnels and quantum-resistant cryptography.
Our Zero-Trust approach ensures that every user and device is authenticated and authorized before accessing any resource, minimizing the risk of data exposure. By implementing quantum-resistant cryptography, we further protect against future threats, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of your data.
Moving Towards Usernames
To address data scraping concerns, WhatsApp is considering the use of usernames instead of phone numbers as the primary identifier in the app. This would limit the ability to enumerate user accounts and reduce the risk of data exposure.
WhatsApp has started testing a username feature in beta, which may offer a better approach to privacy.
Gopher Security's Role
Gopher Security offers advanced solutions to protect against similar vulnerabilities. Our AI-powered platform provides:
- Continuous monitoring and threat detection
- Automated incident response
- Zero-Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
- Quantum-resistant encryption
By partnering with Gopher Security, organizations can enhance their security posture and protect against emerging threats like those exploited in the WhatsApp vulnerability.
Don't wait for the next data breach. Explore how Gopher Security's Zero-Trust architecture can safeguard your organization. Contact us today to learn more.





