Protect Yourself from Callback Phishing Scams: Key Tips and Examples
Callback Phishing Scams Overview
Callback phishing scams are a growing threat, leveraging social engineering tactics to deceive individuals into calling a phone number provided in a fraudulent email. These scams often impersonate well-known brands, creating a false sense of urgency to extract sensitive information. According to a report from Cisco Talos, malicious emails are often designed to look like they come from trusted companies like Microsoft, Adobe, and PayPal. They typically contain information about an account issue or an upcoming transaction, urging the recipient to call a listed number for resolution.

Image courtesy of Lifehacker
Once victims are on the phone, scammers pose as customer service agents and may attempt to gather personal information or direct individuals to malicious websites. A significant tactic used is attaching a PDF that loads automatically, circumventing email security features which usually scan for text and links.
Recognizing Callback Phishing Red Flags
It is crucial to be aware of the signs indicating a potential callback phishing scam. Red flags include:
- Urgent communication that incites fear or confusion.
- Emails containing attachments that automatically load.
- Requests for sensitive information over the phone.
Individuals should never click links or scan QR codes from emails or texts until verifying the sender through official channels. Email addresses can be spoofed, making it essential to independently verify any request before taking action.
For further insights, refer to Lifehacker's guide on avoiding phishing scams.
Real-Life Callback Phishing Examples
Numerous tactics are employed in callback phishing scams, including:
- Fake Subscription Renewals: Attackers send emails about urgent renewals for software, providing a phone number to cancel. When victims call, scammers gather sensitive data.
- Impersonated Bank Alerts: Emails claiming unusual transactions prompt employees to call a “secure” number. Scammers extract sensitive account details under the guise of verification.
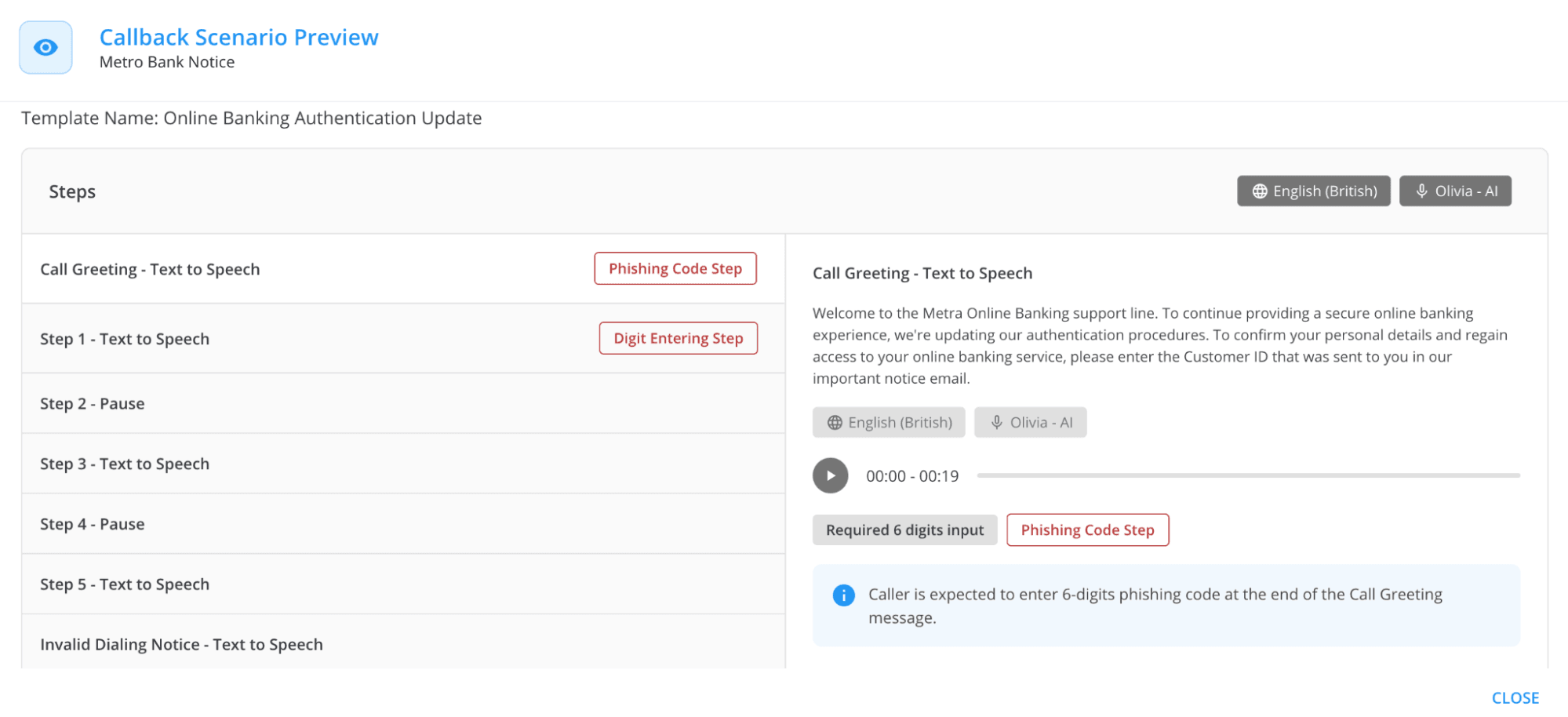
Image courtesy of Keepnet
- CEO Impersonation Scams: Attackers impersonate company executives, claiming urgent wire transfers need processing. Victims are tricked into transferring funds.
- Fake Vendor Invoices: Attackers send invoices from spoofed addresses with a provided callback number for verification, collecting sensitive financial data.
- Technical Support Scams: Phishing emails warn of critical system issues, prompting employees to call for help and provide login credentials.
Organizations can mitigate risks through security awareness training and phishing simulations.
How Callback Phishing Affects Organizations
Callback phishing poses significant risks, including:
- Data Breaches: Employees inadvertently disclose confidential information.
- Reputation Damage: Successful phishing attacks erode client and partner trust.
- Financial Losses: Organizations incur costs from fraud and recovery efforts.
Companies should implement strategies such as incident response planning and human risk management to strengthen their defenses against these threats.
Protecting Against Callback Phishing
As the risk of callback phishing increases, organizations must adopt effective defense strategies. Keepnet offers a Callback Phishing Simulator with customizable templates, allowing realistic training for employees. This training equips staff to recognize and respond to phishing attempts effectively.
For further reading, explore Keepnet's comprehensive article on the most common examples of phishing emails.
Practical Tips for Individuals
To safeguard against callback phishing scams, individuals should:
- Avoid calling numbers from suspicious emails. Instead, verify through official company websites.
- Never allow remote access to devices unless initiated by a trusted service.
- Pause and verify any urgent requests before taking action.
For more cybersecurity insights, consider submitting inquiries about suspicious emails to your organization's security team for investigation.
Explore the services offered by Gopher Security to learn more about safeguarding against phishing threats.





