React2Shell CVE-2025-55182: Max-Severity Threat to JavaScript

TL;DR
- This article details critical vulnerabilities affecting n8n automation platforms and React Server Components. CVE-2026-21858 in n8n allows unauthenticated attackers full network control, impacting approximately 100,000 servers. The React2Shell vulnerability (CVE-2025-55182) is a CVSS 10.0 RCE exploit leading to post-exploitation activities like malware deployment and data theft. Urgent patching and WAF implementation are strongly advised for both.
Critical Vulnerability in n8n Automation Platform
A critical vulnerability, CVE-2026-21858, has been identified in n8n, an automation platform used to integrate AI agents and other enterprise services. The vulnerability affects approximately 100,000 servers globally. Discovered by Cyera, the flaw allows attackers to gain full control of targeted networks. A patch was released on November 18, but public disclosure was delayed.
According to Dor Attias, security researcher at Cyera Research Labs, "Gaining control of n8n means gaining access to your secrets, customer data, CI/CD pipelines and more." While active exploitation hasn't been confirmed, a proof of concept is available, increasing the urgency for patching. Upwind CEO Amiram Shachar noted a rise in traffic targeting n8n instances. The vulnerability is a content-type confusion issue requiring no authentication and allowing remote code execution with no workaround besides patching. Users are advised to update to version 1.121.1 or later.
Another remote code execution vulnerability, CVE-2026-21877, with a CVSS rating of 10, was also disclosed.
React2Shell Fallout and Exploitation Surge
The React2Shell vulnerability (CVE-2025-55182) continues to impact numerous organizations, with a high number of publicly available exploits. Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 reports over 60 organizations affected.
Microsoft found "several hundred machines across a diverse set of organizations" compromised via remote code execution, leading to reverse shell implants, lateral movement, and data theft. VulnCheck confirmed nearly 200 valid public exploits. React also disclosed three new defects (CVE-2025-55183, CVE-2025-67779, and CVE-2025-55184).
Google Threat Intelligence observed financially motivated attackers and Chinese espionage groups exploiting the vulnerability. Amazon reported exploitation attempts by Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda. S-RM responded to a ransomware attack involving React2Shell. Cloudflare noted targeting of networks in Taiwan, Xinjiang Uygur, Vietnam, Japan, and New Zealand, as well as U.S. government websites and critical infrastructure. GreyNoise is seeing high exploitation rates.
PeerBlight Linux Backdoor Exploiting React2Shell
Huntress has observed threat actors exploiting CVE-2025-55182 to deploy a Linux backdoor, a reverse proxy tunnel, and a Go-based post-exploitation implant. The vulnerability, dubbed “React2Shell”, exists due to insecure deserialization in React Server Components.
Observed post-exploitation activities include:
- Deployment of cryptominer malware.
- Deployment of a Linux backdoor tracked as PeerBlight, using the BitTorrent DHT network as a fallback C2 mechanism.
- Use of a reverse proxy tunnel called CowTunnel, connecting to attacker-controlled FRP servers.
- Deployment of a Go-based post-exploitation implant dubbed ZinFoq, featuring reverse shells, SOCKS5 proxying, and timestomping capabilities.
- Distribution of a Kaiji botnet variant with DDoS capabilities and hardware watchdog abuse.
React2Shell exploits React Server Components’ processing of the React Flight protocol. The vulnerability allows untrusted code execution or exposure of secrets/credentials. The attacker crafts a Chunk that includes a “then” method, tricking React into executing malicious code.
Vercel's Response to React2Shell
Vercel reports blocking over 6 million exploit attempts targeting vulnerable Next.js deployments. They worked with 116 security researchers, paying out over $1 million and shipping 20 unique WAF updates in 48 hours.
Vercel emphasizes that CVE-2025-55182 is a critical vulnerability requiring immediate action. Vercel AI Cloud provides tooling, infrastructure, and developer experience to simplify AI application development. They also offer zero-config backends for Python and TypeScript backend frameworks.
React2Shell: A CVSS 10.0 RCE
React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182) is a maximum-severity remote code execution vulnerability affecting React Server Components. It allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTTP request. Shadowserver reports 77,664 vulnerable IP addresses. Palo Alto Networks confirmed over 30 compromised organizations.
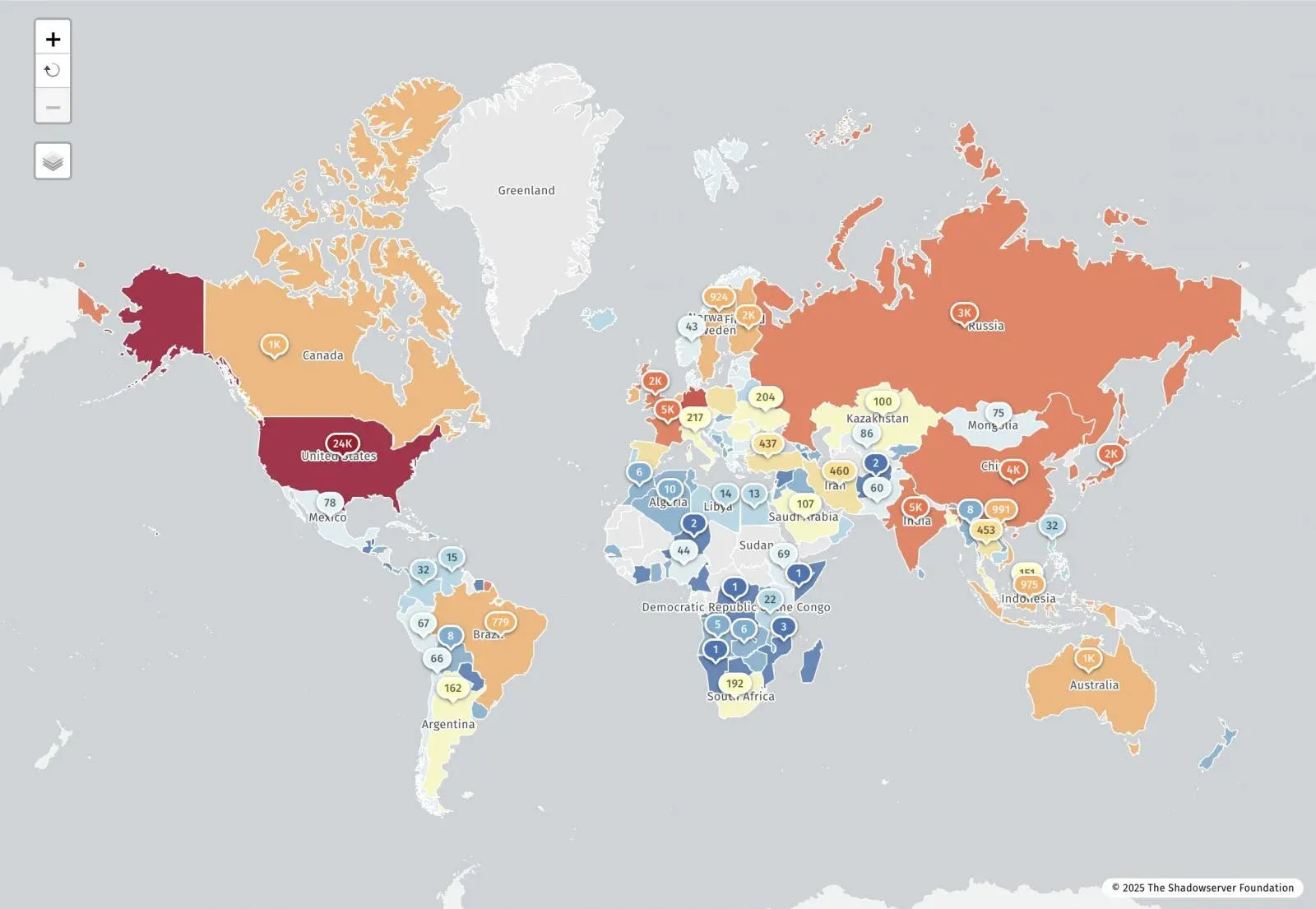
Chinese state-nexus threat groups began exploiting the vulnerability within hours of public disclosure. CISA added it to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. A publicly available Chrome extension automates scanning and exploitation of vulnerable sites. The vulnerability stems from unsafe deserialization in the React Server Components "Flight" protocol. Lachlan Davidson, who discovered the vulnerability, has created a resource to track it.
Remediation Steps
- Update React Packages:
npm install react@latest react-dom@latest react-server-dom-webpack@latest - Update Next.js:
npm install [email protected] # for 15.0.x npm install [email protected] # for 15.1.x npm install [email protected] # for 15.2.x npm install [email protected] # for 15.3.x npm install [email protected] # for 15.4.x npm install [email protected] # for 15.5.x npm install [email protected] # for 16.0.x - Deploy WAF Rules: AWS WAF, Google Cloud Armor, Vercel, and Fastly have deployed protective WAF rules.
These widespread vulnerabilities highlight the need for robust cybersecurity solutions. At Gopher Security, we specialize in AI-powered, post-quantum Zero-Trust cybersecurity architecture. Our platform converges networking and security across devices, apps, and environments, using peer-to-peer encrypted tunnels and quantum-resistant cryptography.
Explore our services and contact us at Gopher Security to learn more about how we can help protect your organization.